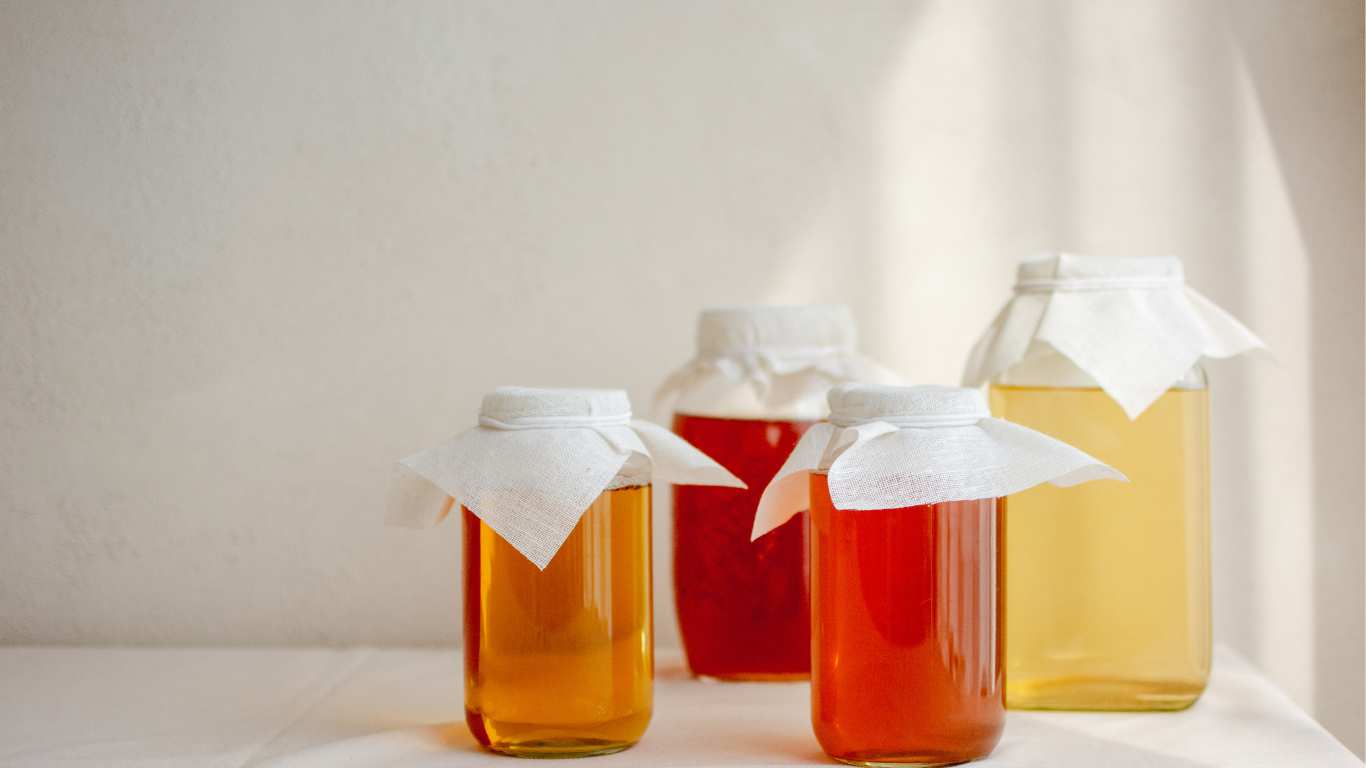
In the world of fermenting food, the choice between glass and plastic vessels holds significant importance. This is because the right container can significantly impact the quality, safety, and outcome of the fermentation process. This brings us to the important debate- glass vs plastic for fermenting food: which is better?
Between glass and plastic, it is better to ferment food in glass containers. Both materials have their advantages and drawbacks. However, the safest and most optimal fermentation results can be done by fermenting your food in glass containers.
Whether you’re making sauerkraut, kimchi, kombucha, or beer, choosing the right vessel for fermentation is crucial. Especially for amateur fermenters and home cooks, knowing all about fermenting in both glass and plastic containers is essential. So, let’s dive into it.
Is It Better To Ferment Food In Glass Or Plastic
It is better to ferment food in glass containers in comparison to plastic containers. Glass also will last very long to get the best results from fermenting your food. Its impermeability to oxygen, ease of cleaning, longevity, and transparency make it the preferred choice for fermenters.
Both glass and plastic offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, making the decision a nuanced one that requires careful evaluation.
Glass
Glass fermentation vessels, such as carboys, mason jars, or fermentation crocks, are celebrated for their inert nature and transparency. They provide an impermeable barrier against oxygen, which is crucial for successful fermentation.
The ability to observe the fermentation process through transparent glass allows fermenters to monitor progress without compromising the integrity of the environment. Glass is also relatively easy to sanitize and maintain due to its non-porous surface. However, glass vessels tend to be heavier and more fragile than their plastic counterparts, requiring careful handling.
Additionally, glass is sensitive to light, necessitating protection from harmful UV radiation during fermentation.
Plastic
Plastic fermentation containers, such as buckets or bins, offer practical benefits such as lightweight construction, durability, and affordability. Plastic is less prone to shattering than glass, making it a safer option for those concerned about accidental breakage.
Plastic containers are also easier to transport and handle, particularly for large-batch fermentations. However, plastic is slightly permeable to oxygen, which may impact certain fermentation processes. Plastic containers do not offer the same level of transparency as glass, limiting direct observation of the fermentation process.
Scratches in plastic containers can create small crevices where bacteria can hide and grow, even after regular washing. Over time, this can lead to contamination and potential health risks. It’s a good idea to inspect plastic containers regularly for scratches and consider replacing them if they become too worn.
So, when deciding between glass and plastic for fermenting food, we should consider all the important factors before. In the end, glass stands out as the best choice for fermenting food. It keeps oxygen out, cleans easily, lasts longer than plastic, and lets you see what’s happening inside. This can ensure your fermentation projects stay safe and healthy over time.

What Materials Cannot Be Used In Ferment?
The materials that we cannot use in fermentation include reactive metals such as aluminum, copper, and cast iron. Additionally, galvanized metal, often coated with zinc, brass, and bronze, containing copper, ceramic, or pottery vessels glazed with lead, wood vessels, etc. materials should be avoided.
When it comes to fermentation, selecting appropriate materials for fermenting vessels and utensils is crucial to ensuring the safety and quality of the final product. Certain materials should be avoided due to their negative consequences. These materials possess the potential to react with fermenting ingredients, compromising the integrity of the ferment and posing health risks.
One of the primary materials that we cannot use in fermentation is reactive metals such as aluminum, copper, and cast iron. These materials can undergo chemical reactions with acidic foods or liquids commonly used in fermentation. These reactions can result in off-flavors and potential health hazards that can ultimately ruin the whole process of fermentation.
Additionally, galvanized metal, often coated with zinc, presents a similar risk, as zinc can leach into the ferment when exposed to acidic conditions. This poses potential health concerns. Brass and bronze, containing copper should also be avoided in fermentation vessels and utensils.
Furthermore, ceramic or pottery vessels glazed with lead-based coatings pose a significant hazard leading to severe health consequences upon consumption. Finally, wood treated with toxic chemicals or finishes should be excluded from fermentation processes. Because these chemicals can contaminate the ferment and compromise its safety.
What Can I Use To Keep The Ferment Submerged?
To keep the ferment submerged during the fermentation process, there are several options you can consider. You can choose them depending on your preference and the type of ferment you are making. So, here are some common methods that you can look further into.
Fermentation Weights
Fermentation weights are specifically designed to keep vegetables submerged beneath the brine during the fermentation process. They come in various shapes and materials, including ceramic disks, glass weights, or stainless-steel weights. These weights are typically placed directly on top of the vegetables inside fermentation crocks or jars to prevent the vegetables from floating to the surface.
Fermentation weights offer several advantages. They distribute pressure evenly across the surface of the vegetables, ensuring consistent submersion and preventing exposure to oxygen. High-quality fermentation weights are made from non-reactive materials such as ceramic or glass, which do not leach any harmful substances into the ferment.
They are easy to clean and sanitize, making them a convenient option for home fermenters. These weights are especially popular for fermenting vegetables like sauerkraut, kimchi, and pickles, where it’s essential to keep the vegetables submerged. In this way, you can promote a healthy fermentation environment.
Ziplock Bags filled with Brine
Another common method for keeping ferments submerged is to use ziplock bags filled with brine (salt water). After placing the vegetables and brine in the fermentation vessel, fill a ziplock bag with additional brine and seal it tightly. Then, place the bag on top of the vegetables, pressing them down and ensuring they remain submerged beneath the brine.
Using ziplock bags filled with brine offers several benefits. Ziplock bags are readily available and can be easily customized to fit different fermentation vessel sizes. You can control the amount of brine in the bag to adjust the weight and ensure proper submersion of the vegetables. Ziplock bags are affordable and accessible, making them a budget-friendly option for home fermenters.
This method is particularly useful for ferments like krauts and kimchi, where the weight needs to be adjusted to accommodate the expanding gases produced during fermentation. Place a ziplock bag filled with brine (salt water) on top of the vegetables to act as a weight. Ensure that the bag is sealed tightly to prevent leakage and contamination. This will ensure a successful fermentation.
Fermentation Lids with Built-in Weights
Fermentation lids with built-in weights represent a modern and convenient solution to the age-old challenge of keeping vegetables submerged beneath the brine during fermentation. These specialized lids are designed with innovative features that ensure that the fermentation process is optimal and successful.
Unlike traditional methods, fermentation lids automatically apply gentle pressure to the fermenting vegetables, keeping them below the surface of the brine. The integrated weights apply uniform pressure across the entire surface of the fermenting vegetables. This minimizes the risk of uneven fermentation or exposure to oxygen.
Thus, fermentation lids with built-in weights help promote a more controlled and predictable fermentation process, resulting in consistent flavor development and microbial activity. This helps promote a more controlled and predictable fermentation process, resulting in consistent flavor development and microbial activity.
Conclusion
Both glass and plastic containers have their place in home fermentation. So, make sure to consider your specific needs, batch size, and handling preferences.
Whichever you choose, remember that proper sanitation and care are essential for successful fermentation. So, whether you’re a glass enthusiast or prefer the practicality of plastic, happy fermenting!